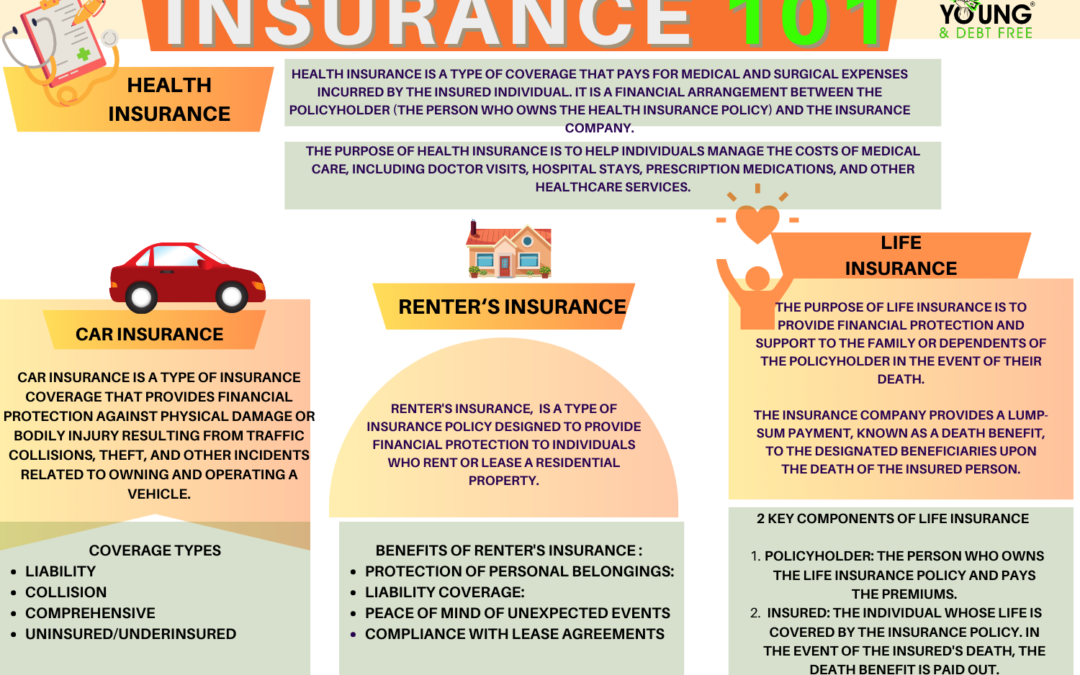
Life insurance is a financial contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurance company provides a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to the designated beneficiaries upon the death of the insured person. The purpose of life insurance is to provide financial protection and support to the family or dependents of the policyholder in the event of their death.
Key components of life insurance include:
- Policyholder: The person who owns the life insurance policy and pays the premiums.
- Insured: The individual whose life is covered by the insurance policy. In the event of the insured’s death, the death benefit is paid out.
- Beneficiary: The person or entity designated by the policyholder to receive the death benefit. Beneficiaries are typically family members or dependents who would face financial challenges in the absence of the insured.
- Premium: The regular payments made by the policyholder to the insurance company to maintain coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, annually, or according to other agreed-upon schedules.
- Death Benefit: The amount of money paid to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. The beneficiaries receive this lump-sum payment tax-free, and it is intended to help cover funeral expenses, replace lost income, pay off debts, or meet other financial needs.
There are several types of life insurance, including:
- Term Life Insurance: Provides coverage for a specified term, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured dies within the term, the death benefit is paid; otherwise, the coverage expires.
- Whole Life Insurance: Offers coverage for the entire life of the insured, as long as premiums are paid. It also has a cash value component that grows over time and can be accessed by the policyholder.
- Universal Life Insurance: Combines a death benefit with a savings or investment component. Policyholders have flexibility in adjusting premium payments and death benefits.
- Variable Life Insurance: Allows the policyholder to invest the cash value in various investment options, exposing the policy to potential market fluctuations.
Life insurance is an important financial tool for those who want to ensure financial security for their loved ones in case of unexpected death. The choice of the type and amount of coverage depends on individual circumstances, financial goals, and preferences. It’s advisable to carefully review and understand the terms of the policy before purchasing life insurance.